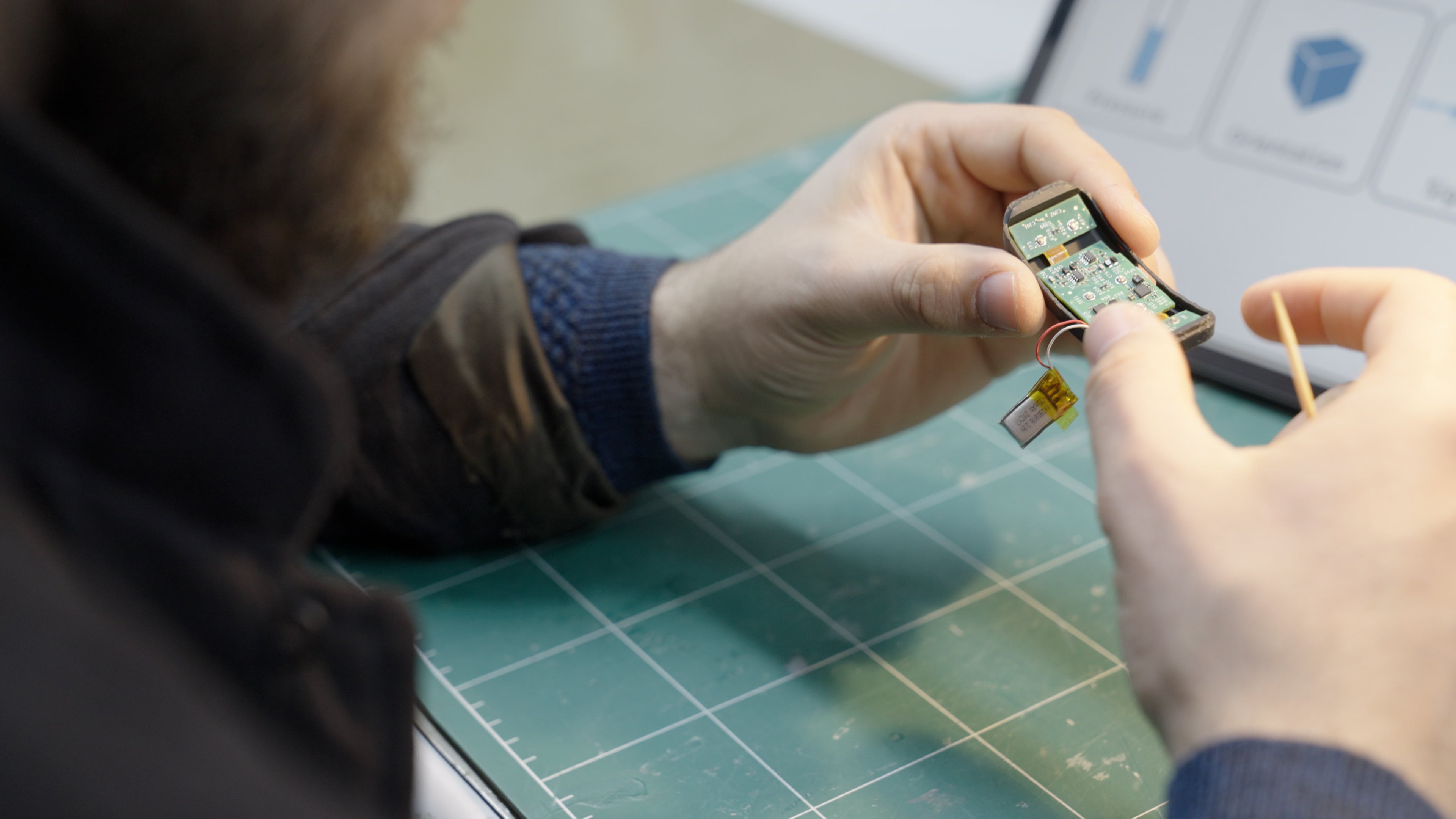
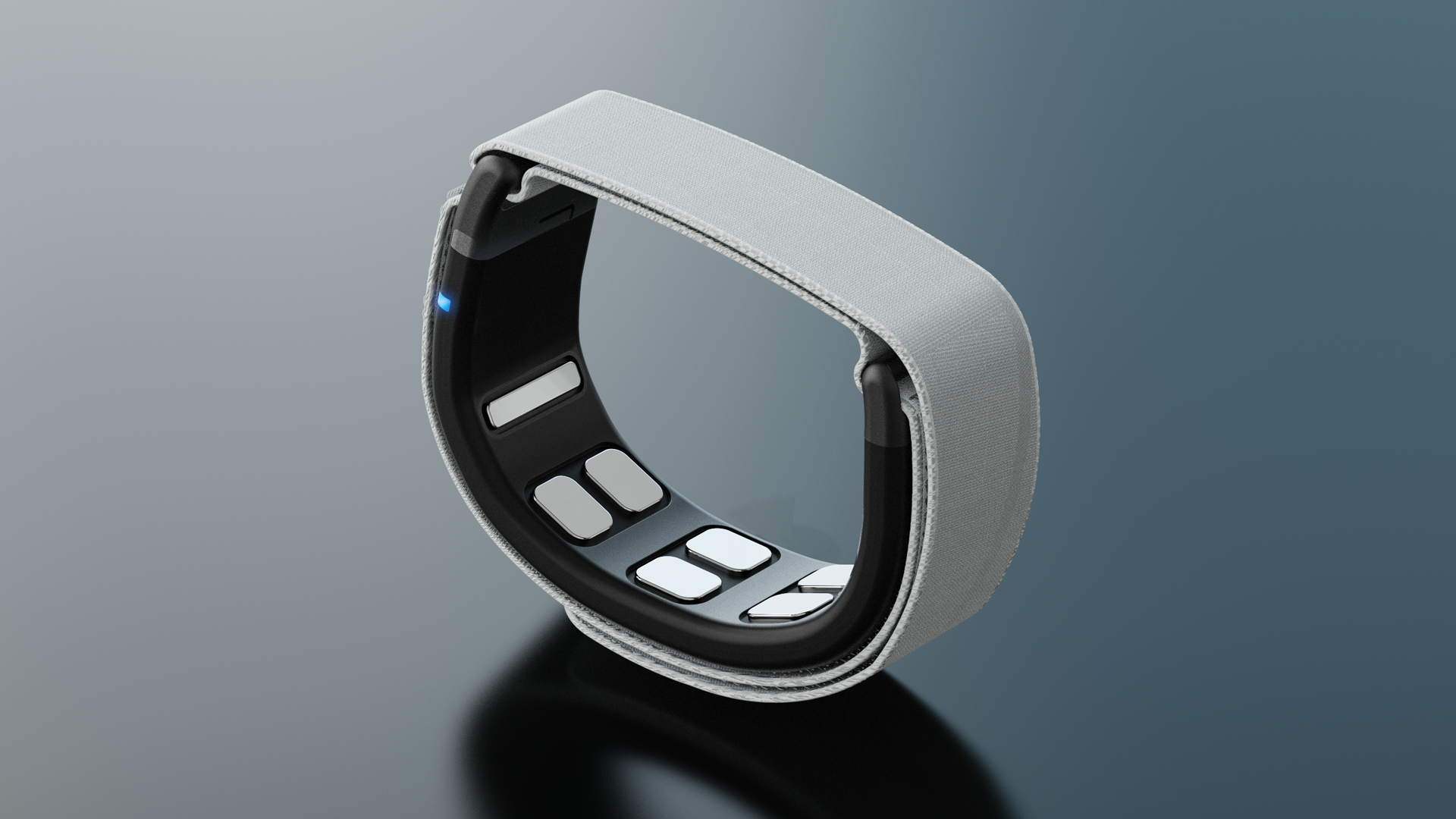
EMG WRISTBAND
This is how it works:

1. Neural Command Initiation
Every movement begins in the motor cortex, the brain region responsible for planning and executing voluntary motion. When you decide to move your hand, electrical impulses (action potentials) are generated in motor neurons and sent down the spinal cord. These signals travel through peripheral nerves to reach the muscles in your forearm and hand.

2. Muscle Activation & MUAP Generation
Upon reaching their target, these neural signals activate motor neurons, which in turn stimulate muscle fibers. This activation leads to muscle contraction and the production of tiny electrical currents called motor unit action potentials (MUAPs). These signals propagate through soft tissue and reach the skin’s surface, where they can be detected.

3. EMG Signal Capture with Mudra Wristbands
Mudra EMG wristbands, including both Mudra Link and Mudra Band, are equipped with proprietary Surface Nerve Conductance (SNC) sensors that capture the electrical activity generated by muscle contractions via surface electromyography (sEMG).
Although this procedure has long been a staple in scientific research, it now allows for direct measurement of these signals from the wrist.
4. Signal Processing: Amplification, Filtering, & Conversion
The electrical signals detected at the wrist are inherently weak and mixed with various physiological and environmental noises. To ensure accurate interpretation, each device’s processor carries out a multi-step process:
Amplification: Enhances the signal strength for better readability.
Filtering: Removes irrelevant noise from environmental interference or other muscle activities.
Analog-to-Digital Conversion: Transforms the bio-potential signals into digital data that can be analyzed by neural networks.

5. AI-Powered Gesture Recognition
The embedded processor in each Mudra EMG wristband employs AI algorithms trained on vast datasets of diverse gestures. By recognizing the state of the sensor array and the patterns within the bioelectrical signals, it classifies them into distinct gesture commands, such as a tap, swipe, or pinch. This real-time classification enables smooth and intuitive control of connected devices with minimal effort.
6. Low-Latency Command Transmission via BLE
Once a gesture is classified, the wristband transmits the corresponding digital command via Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) to your device. BLE ensures an energy-efficient, low-latency connection, allowing for responsive and seamless control of smartphones, AR glasses, and other digital interfaces.