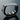In Meta Connect 2024, Mr. Mark Zuckerberg unveiled Orion - ‘a purposeful prototype’ headset that combines augmented reality glasses, generative AI, eye and hand tracking, and a gesture control wristband. Weighing at around 100 grams (3.5 ounces), Meta's Orion AR glasses are designed to be lightweight and comfortable for extended use, while still packing advanced display and tracking technology for an immersive augmented reality experience.
Orion comes with three components: the glasses, the puck, and the wristband. The glasses use waveguide optics and micro-LED displays to project AR content. The puck functions as an external processing unit to handle computational tasks. The wristband tracks hand gestures for interaction with the AR system.

The Orion smart glasses alongside the wristband and wireless compute puck.
Image Credits: Mets
The Basics of Human-Computer Interaction
Navigating and pointing are fundamental to Human-Computer Interaction (HCI), enabling users to explore and interact with digital spaces intuitively. Navigation is about moving within these spaces, like scrolling through a webpage or moving in a virtual environment. Pointing focuses on precision—selecting or manipulating digital elements, such as clicking on links or interacting with virtual objects.
The most common pointing device, a.k.a. Human-Interface Device (HID), is the computer mouse. Other common pointing device products are the directional pad and gaming controller. Newer input devices include trackpad and touchscreen, gesture recognition cameras and radars, IMU-based wearables, and neural interfaces.
For example, a user operates a computer mouse to control a PC where Navigation is achieved by physically moving the mouse to direct the on-screen cursor, and Pointing involves positioning the cursor over specific elements of the interface for interaction and clicking on a button. On a smartphone touchscreen, Navigation is achieved by swiping or scrolling with their finger to move through different screens or content, and Pointing involves tapping on specific elements of the interface, like icons or buttons.
For some cases the interface may include additional, programmable buttons or gestures that offer quick access to common tasks, enhancing efficiency. Examples include: back/forward, volume control, media control. An effective Graphical User Interface (GUI) design ensures that navigation is seamless, and pointing actions like clicking or tapping are straightforward, enhancing overall user experience and accessibility.
Meta Neural Wristband Gestures
As published, navigation on the Orion AR glasses is achieved through gaze detection where the user uses the eyes to focus on certain digital elements. The wristband is used for pointing. The combination of gaze/eye-tracking for navigation and gestures for pointing has been hailed on the Apple Vision Pro (AVP), even though AVP relies on cameras to detect the gestures, as we’ve thoroughly covered on our 'How to Interact with the Apple Vision Pro Using Gestures' blog post.
The main gesture the Meta neural wristband recognizes are:
- Tap - pinching your index finger with the thumb to Select
- Middle Tap - pinching your middle finger with the thumb to invoke the Main Menu
- Thumb Flicks - thumb pushes (flicking, as if tossing a coin) against the closed palm to scroll up, thumb pushes down to scroll down
- Double Thumb - quick double thumb tap on the middle finger to launch Meta AI
Based on the above, we can summarize that the Tap and the Thumb Flick gestures are the equivalent of tap and scroll, and the thumb flick gestures are the programmable gestures which are unique to the Orion AR glasses GUI and OS.
Mudra Band and Meta Neural wristband - Gesture comparison
To better understand the gestures used in these devices, we've created a comparison table:
|
Function |
Mudra Band (iPhone) |
Meta Neural Wristband |
|
Navigate |
By moving the wrist. |
By looking at an item using eye-tracking. |
|
Select |
Tap your index and thumb fingers together. |
Tap your index and thumb fingers together. |
|
Scroll up |
Pinch and quickly flick your wrist up. |
Thumb pushes outwards against the closed palm. |
|
Scroll down |
Pinch and quickly flick your wrist up. |
Thumb pushes outwards against the closed palm. |
|
Main menu |
Twist of the wrist. |
Pinch the middle finger with the thumb |
|
Meta AI |
- |
Quick double thumb tap to launch Meta AI |
|
Swipe left or right |
Pinch and quickly flick your wrist sideways. |
- |
Spatial Gestures using the Mudra Band
Where can you experience these gestures?
The Meta Orion is considered ‘a purposeful prototype’ with no actual time-to-market, and with the Apple Vision Pro priced at $3,499, can you get a neural wristband to experience wearable gesture control, today?
Yes. We’ve got you covered!
The Mudra Band is a neural input watchband for the Apple Ecosystem. It allows users to control devices like Apple TV, Mac computer, iPad, iPhone and Vision Pro through familiar gestures and comfortable body postures. With its customized Watch face, users can hop and switch control between their Apple devices simply by tapping on an icon in the watch face.
The Mudra Band is available today and is shipped within 5 business days. Learn more here.
The Mudra Link is a revolutionary neural interface wristband that allows you to control your computers and devices using nothing more than simple hand gestures. Mudra Link is not just another wearable; it’s a groundbreaking extension of your hand, translating subtle movements into powerful commands. It will include a mapper which enables you to bind specific gestures with customized functions.
The first Mudra Link product batch will be shipped in January 2025. Pre-order here.
Whether you want the Mudra Band gracing your wrist by next week or to wait until you get the Mudra Link, we offer a 10% discount on all your product orders at www.mudra-band.com. Use the link or use promo code SAVE10 at checkout.